Tips on how to Write Horror: eight Essential Elements to Terrify and Delight
The horror genre might call to mind slasher films or other monster movies your teenage friends made you watch at night to scare you out of your wits. But horror is more than a shock fest. Scary stories have the ability to reveal the human condition in ways many other genres cannot. Today let’s look at how to write horror.
Types of stories
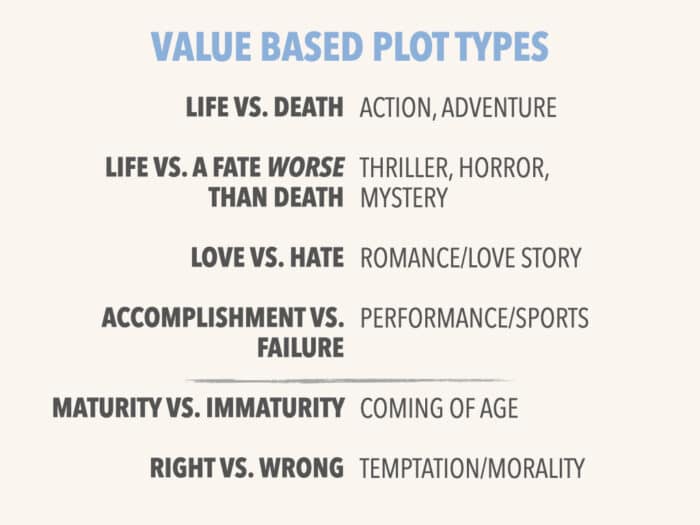
We’re continuing our series on how to write each of the ten types of stories, based on values. Values are defined by what a character wants or needs most in a story. Story types can defy genre boundaries which are often more about reader expectations and specific tropes, but the two often work together to create a satisfying reader experience.
Here are the six value scales with the plot types they tend to fall into:
- Survival from Nature > Life vs. Death
- Survival from Others > Life vs. Fate Worse than Death
- Love/Community > Love vs. Hate
- Esteem > Accomplishment vs. Failure
- Personal Growth > Maturity vs. Immaturity
- Transcendence > Right vs. Wrong
With that in mind, let’s delve into how to write a horror book or story.
What is horror?
Horror is a genre of literature or film that wants to evoke fear, shock, and suspense. Characters battle for their life versus a fate worse than death.
What does that mean? A fate worse than death can mean everything from experiencing embarrassment to paralyzing fear to pain to a loss of innocence.
There are many types of horror sub-genres, ranging from psychological horror to horror comedy to cosmic horror, to slashers and body horror. Horror stories often (but don’t have to) have supernatural horror elements, such as ghosts, monsters, vampires, and witches.
Common techniques used to create horror include jump scares, gore, unexpected twists, isolation, and eerie sound effects. Writing horror successfully requires an understanding of human psychology and the ability to create tension and suspense through careful pacing and narrative structure.
Horror isn’t just about gore or terror, however. Many horror stories include societal, environmental, or psychological themes.
To write effective horror stories, authors must be able to craft believable characters that audiences can sympathize with as well as build suspense through cleverly crafted plots.
An Example of Master Horror Fiction: Poe
Edgar Allan Poe’s story “The Tell Tale Heart” is a story most of us read in school. If you haven’t read it or you need a refresher, read it for free on Guttenberg.
“The Tell Tale Heart” is narrated by an unreliable, unnamed narrator who is confessing to a murder, while simultaneously trying to prove he’s not insane. He’s killed an old man, whom he supposedly loved, because the man’s eye creeped him out. The police show up, and he’s calm and collected until he thinks he can hear the old man’s heart beating under the floor boards. The beating gets louder until the man confesses to the police, begging them to make the noise stop.
This story packs all the elements of horror into around 2,000 words. The unreliable narrator gives readers a sense of unease and ambiguity throughout the story. Is the man actually mad or is there something supernatural happening?
We have fear, both from the narrator (that creepy eye) and from the old man, who is blind and suspects someone is watching him. We have a murder with dismemberment. We have isolation, as the old man is alone, but the narrator also complains of being scared in the dark night by himself.
Most of all, though, we are on the life vs. fate worse than death scale. The narrator is scared of being seen as insane, which is worse than death for him and is the cause of his confession. He still ends up arrested for the murder, though, which is also a fate worse than death.
What Makes a Good Horror Story?
What makes a good horror story is the ability to tap into our deepest fears and deliver them in a captivating way. Even if you don’t consider yourself a horror writer, practicing a few short stories in this genre can help you understand human fear and the way it motivates action.
Setting and atmosphere
A good horror story should start off slow, introducing the characters and setting of the story before slowly building up tension as the horror begins to unfold. The setting of horror stories is often mundane and familiar initially—a summer camp, a basement, a house—but turns sinister as the story progresses.
The more the reader or audience can relate to the setting, the scarier it will be when the protagonist encounters anything spooky. Use sensory details to build the atmosphere. Old houses or rundown buildings and impending bad weather are common in horror stories.
- Bram Stoker’s Dracula begins with Jonathan Harker arriving at Dracula’s castle, which is isolated, rundown, and surrounded by fog.
- Movies like The Conjuring and Poltergeist (and a ton of others) start by a family moving into a new house.
- Midsommar begins in a seemingly idyllic community.
- A lot of horror—like The Shining—uses an impending storm to indicate coming doom. The crescendo of the storm culminates in the climax.
Believable character
Characters should be relatable and sympathetic so that readers can connect with them on an emotional level. Readers need to care about what happens to them in order for the horror to be effective. Develop their backstories and motivations, so that when terrible things happen to them, it feels like a genuine tragedy.
- The Mist by Stephen King opens with a man cleaning up his property after a weird storm. We’re introduced to the entire family and a neighbor and have a chance to learn the dynamics there before any of the true action happens.
- Danny in The Shining is a rather lonely little boy who has an alcoholic for a father. The reader can’t help but want to protect him. His mother is hoping the move to the Overlook will cure their family. This broken family makes Jack’s devolution more horrifying and tragic.
Fleshed out antagonist
The antagonist should be well-crafted and have both human qualities and monstrous ones; this will help create a sense of dread in readers as they don’t know what to expect from the villain. Ensure that your antagonist is well-rounded and has their/its own motivations, even if that motivation is something as simple as eating or breeding.
- The antagonist in the movie Species starts off as an alien-human hybrid lab experiment. Her core motivation is procreation and because of how she was treated by her captors in her backstory, any human sympathy she might have had is nullified in her quest.
- In The Creature from the Black Lagoon, Gillman just wants people to leave his territory and to be left alone (preferably with Kay, who he’s rather smitten with).
- In Stephen King’s Misery, Annie Wilkes wants to save her favorite author (and maybe keep him around a bit longer than necessary initially), then desperately wants to save her beloved book series.
- Hannibal Lector is a culturally refined, brilliant, manipulative cannibal who held a prestigious place in his profession and prefers to eat the rude. In later stories, we discover he was traumatized as a child.
Foreshadowing
Use subtle hints or clues that something scary is about to happen. Foreshadowing can create a sense of anticipation and dread in the audience. Some common elements of foreshadowing in horror include: mysteriously locked doors, getting a chill for seemingly no reason, something being where a character didn’t think they left it, hearing a strange noise, being warned off by the locals, or learning early on of a historic tragic event.
- In The Shining, we’re told if there’s a snowstorm no one would be able to get to the hotel. Jack is also warned by the hotel owner that the former caretaker killed his family before taking his own life.
- In The Haunting of Hill House, Eleanor receives warnings in the form of signs reading “Dare” and “Evil” and someone telling her she will be sorry the gate was ever opened. (In the Netflix series based on this book, there are ghosts hidden in corners and out of focus in many scenes.)
No help in sight
As your story progresses, your characters can’t simply call the police or go to a neighbor for help. If that were the case, the horror would be over in a few minutes and the story would end. It should look increasingly doubtful that your characters will escape their situation. Isolation—physical or psychological/emotional—is a common way to achieve this.
- Nick Cutter’s The Troop places a boy scout troop on a remote island with only one adult. When the adult is removed from the storyline, the boys are left on their own to battle a parasitic outbreak.
- Stephen King’s The Shining takes place at a remote hotel during the offseason and gets worse when a blizzard traps the Torrances.
- Most R.L. Stine books feature children who aren’t physically isolated from others, but the adults don’t believe them and therefore aren’t going to help.
- Zoje Stage’s Baby Teeth features parents who can’t control their nightmare child. The help they do receive doesn’t work.
- In The Texas Chainsaw Massacre, any hope of help is dashed as the main character slowly realizes everyone in town is the enemy.
Deeper themes and ideas
Horror can be a powerful tool for exploring deeper themes and ideas. Use your writing to explore issues like mortality, identity, and the human condition. Don’t just rely on jump scares and gore, but instead use horror to tell a compelling story with something to say.
- Most vampire stories are about addiction and/or the rich literally sucking the life out of the poor.
- The 2022 movie Smile is about the “contagious” nature of trauma and generational trauma.
- Stories like The Blob, Resident Evil, Frankenstein, and Mira Grant’s Parasitology series warn about science gone wrong.
Effective pacing
Effective horror requires careful pacing. You don’t want to reveal too much too soon, but you also don’t want to drag things out for too long. Use pacing to build tension and create a sense of urgency.
Keep your readers guessing and eager to find out what happens next. But don’t exhaust them; every scene shouldn’t be one of terror. In fact, the jump scares and ghost sightings aren’t how you scare your readers. The more important part of horror is when you slow down and give your reader room to explore and get comfortable. Then you pull out the monster.
- In The Mist, a strange mist descends while David and his son are in the grocery store.
- A man runs in and says someone disappeared in the mist. (Faster.)
- Everyone agrees to stay put for a while. Things calm for a moment. (Slower.)
- Then they go to the back to fix something, and a man is pulled away by giant tentacles. (Faster.)
- When they tell everyone what happened there are a multitude of reactions, but the point is there is no immediate threat for a while from the monsters. (Slower.)
- Someone decides to lead a group of people outside and they are killed quickly. (Faster.) etc.
See how we’re not seeing the monsters every scene? This gives us as readers (and the characters) time to imagine what the monsters look like, what their motivations are, and to try to come up with a way out. These slower scenes also give us time for some other elements of story, like backstory, tension, and subplots.
Twists, shocks, ambiguity, and everlasting evil
A good horror story should either end with an unexpected plot twist or shock that will leave readers stunned yet satisfied or with an ambiguous ending where the reader is left unsettled because they aren’t positive what happens to the main character.
- In Ania Ahlborn’s The Shuddering, we’re left with imagining what happened to the main character and his dog.
- In Dahl’s The Witches, the reader is left with the image of the boy/mouse and his grandmother bouncing around the world eradicating witches. We don’t know how long they will live (ambiguity), there are still witches, even if they did defeat the specific antagonists for the book (evil still exists), and the boy remains a mouse (twist and shock).
- Every horror movie in a franchise normally ends with the antagonist making an appearance even though they’re supposed to be dead and defeated by the protagonist.
- In Shirley Jackson’s The Lottery, we know exactly what happens, but we have no idea why this stoning ritual is part of this society. We don’t even know when or where this society exists.
How to Write Horror: Lean Into the Fear Factor
Fear is the crucial element in horror story writing. As a genre, horror writing leaves you plenty of room to explore themes and subplots that really dive into the dark fears of your readers—and that creates an emotional experience for your target audience. Even common fears and ordinary situations can turn dark in the hands of a master horror writer.
Dive into your biggest fears to find your best horror ideas. Then share them with us!
Want more horror prompts? Check out our 20 Spine-tingling Horror Story Prompts here.
What fears do you find most compelling in horror? Tell us in the comments.
PRACTICE
Today, tap into that story value of life versus a fate worse than death. Set the timer for 15 minutes and make a list of fears you or a potential character might have and then create a scene where they realize their worst fears are coming true.
Share your practice in the Pro Practice Workshop here, and leave feedback for a few other writers. Not a member? Join us here.
